
diagnosis
the eight pillars
-
exterior
simultaneous chills/fever, superficial pulse, thin tongue coat
chills and fever are subjective sensations experienced by the patient, does not require an actual fever
in some cases acute skin conditions are considered exterior since physical location is on the body's surface
affects: skin, muscles, channels
exterior syndromes are pathological conditions resulting from invasion of the superficial layers of the body. sudden onset. the skin, hair, and muscles belong to the superficial portions of the meridians and collaterals.
symptoms: intolerance of cold, fever with aversion to cold - exterior condition. other manifestations: severe chills, mild fever, no sweating, absence of thirst, headache, general aching, nasal obstruction & cough. thin white tongue coating and superficial pulse.
intermediate
exogenous syndromes, which have failed to fully transmit to the interior. anti-pathogenic qi is not strong enough to expel the pathogen. (shaoyang)
symptoms: alternating chills and fever, discomfort and fullness in the chest and hypochondrium, vomiting, anorexia, bitter taste in the mouth, dry throat, blurred vision and string-taut pulse
interior
fever no chills, or chills no fever, deep pulse, thicker tongue coat
if there is not simultaneous chills and fever the condition is interior
affects: internal organs, bones, qi, blood
affects 5 zang and 6 fu organs. interior syndromes are pathological conditions coming from transmission of exogenous pathogenic factors to the interior of the body. there are three ways they can be transmitted: 1) exterior to interior invading zang-fu 2) direct attack on zang-fu from exogenous pathogenic factors. 3) drastic emotional changes, improper diet, overstrain and stress. changes in the tongue or pulse reflect interior or exterior problems.
symptoms: fever with no aversion to cold or aversion to cold with no fever - interior condition. mild chills, severe fever, no sweating or sweating, thirst. thin yellow tongue coating, superficial and rapid pulse.
-
heat
thirst, fever, aversion to heat, sweating, yellow body fluids, possible constipation, red tongue, yellow or no coat, rapid pulse
exterior heat - fever and chills, more fever than chills, headache, body aches, thirst, sore throat, yellow nasal discharge, thin white or thin yellow coat, possible red tip of tongue, superficial, rapid pulse
treatment principle: promote sweat, clear heat, release exterior
interior heat - aversion to heat, no chills, sweating, red face, yellow sputum, dark yellow urine, constipation, red tongue yellow or no coat, rapid pulse, can also be slippery
treatment principle: clear heat, nourish yin
interior heat can be excess or deficient
excess heat: high fever, entire face is red, thirst for cold fluids, sweating all over body, red tongue, yellow coat, slippery, rapid pulse
deficient heat: low-grade fever in the evening, red cheeks (malar flush), thirst for small sips or thirst for warm water, night sweats, red tongue little or no coat, thready, rapid pulse
true heat, false cold: patient has cold hands and feet, but body is warm, prefers cold drinks, irritability, dry throat, foul breath, yellow urine, red tongue, deep forceful pulse, often seen with liver qi stagnation preventing. yang qi from getting to extremities
may arise from invasion of exogenous pathogenic heat or deficiency of yin in the interior of the body
symptoms: fever, preference for coolness, thirst with preference for cold drinks, redness of the face and eyes, irritability, constipation, deep-yellow and scanty urine; red tongue with yellow, dry coating; rapid pulse
cold
no thirst, chills, clear body fluids, normal or pale tongue, moderate or deep, slow pulse
exterior cold - chills and fever, more chills than fever, headache, body aches, itchy throat, clear nasal discharge, normal thin white coat on tongue, superficial, moderate or superficial, tight pulse
treatment principle: expel wind, release exterior
interior cold - chills, no fever sensation of cold, pale face, frequent clear urine, loose stools, pale tongue, white coat, deep, slow pulse
interior cold can be excess or deficient:
excess cold: sudden, excruciating severe pain, dislike being touched, thick white tongue coat, tight pulse
treatment principle: expel excess cold
deficient cold: dull pain, likes pressure, likes warmth, pale tongue, white coat, deep, slow pulse
treatment principle: warm interior, supplement yang
true cold, false heat: patient has feverishness, flushed face, and thirst, but wants to be covered up, desires warm drink, clear urine, loose stools, pale tongue, white coat, superficial weak pulse
heat above, cold below: heat sensation in chest, thirst, irritability, suffocation, desire to vomit, with loose stools and abdominal pain relieved by warmth
may arise from exterior exposure or from deficiency of yang in the interior of the body
symptoms: aversion to cold, preference for warmth, tastelessness in the mouth, absence of thirst, pallor, cold limbs, lying curled up, loose stools, abundant urine, hot drinks; pale tongue, white moist coat; slow, tense pulse.
-
excess
acute, sudden, vivid, dramatic, solid, full high fever, big thirst, quick changes sharp pain, pain worse with pressure pain eases with movement/sitting food worsens stomach pain sweating, vomiting, bowel mvmt help often overactive shen, agitation thick, sticky tongue coat excess, flooding, full pulse more often affects yang organs
treatment principle: expel or drain excess
deficient
chronic, dull, empty, worse over time low grade fever, minor thirst (if any) mild, achy pain, pain better with pressure, pain better with rest, worse with movement, food helps stomach pain, worse with sweating, vomiting, bowel movement, depleted shen, depression, pale tongue (if qi or blood deficient), weak pulse, usually affects yin organs
treatment principle: nourish deficiency
-
empty (deficiency) yin
white face with red cheeks
low-grade fever in the afternoon, 5 palm heat
night sweats
dry stools
yellow urine
dry throat & mouth
emaciation
red, peeled, dry tongue
floating-empty pulse
most affected organs are kidneys, lung, heart, liver and stomach
empty (deficiency) qi
pale face
weak voice
slight sweating in daytime
bland taste
weak voice, slight breathlessness, tiredness, lack of appetite
empty pulse
most affected organs are spleen and lung
empty (deficiency) yang
all qi symptoms + bright palm face
chilliness, cold limbs
spontaneous sweating
loose stools
frequent pale or clear urine
no thirst, or a desire for hot drinks
lassitude, listlessness
pale, wet tongue
weak pulse
most affected organs are spleen kidneys, lung, heart and stomach
empty (deficiency) blood
dull face, pale lips
insomnia, depression, poor memory, numbness, blurred vision, dry hair
pale, thin tongue
fine or choppy pulse
most affected organs are heart and spleen. if liver involved: blurred vision, depression, numbness, and scanty periods. if heart involved: insomnia and pale face, lips, tongue
-
face
bright-white - full cold (excess yin)
sallow-white - empty-cold (deficiency)
pain
sharp pain, worse on pressure - full cold (excess yin)
dull ache, better on pressure - empty-cold (deficiency)
bowels
better after bowel movement - full cold (excess yin)
worse after bowel movement - empty-cold (deficiency)
thirst
desire to drink warm liquids - full cold (excess yin)
desire to drink warm liquids - full cold (excess yin)
urine
clear abundant urination - full cold (excess yin)
clear abundant urination - empty-cold (deficiency)
pulse
full, tight and deep - full cold (excess yin)
weak, slow and deep - empty-cold (deficiency)
tongue
thick white coating - full cold (excess yin)
thin white coating - empty-cold (deficiency)
-
face
whole face red - full heat (excess yang)
malar flush, dry throat - empty-heat (deficient yin)
eyelid
red all over the inside of the eyelid - full heat (excess yang)
thin red line along inside edge of eyelid- empty-heat (deficient yin)
bowels
constipation, abdominal pain - full heat (excess yang)
dry stool, no abdominal pain - empty-heat (deficient yin)
thirst
desire to drink cold water - full heat (excess yang)
desire to drink warm water, or cold water in sips - empty-heat (deficient yin)
urine
deep-yellow, scanty urine - full heat (excess yang)
yellow urine - empty-heat (deficient yin)
pulse
full-rapid, overflowing - full heat (excess yang)
floating-empty or thin - empty-heat (deficient yin)
tongue
red with yellow coating - full heat (excess yang)
red & peeled, or thin - empty-heat (deficient yin)
taste
bitter taste - full heat (excess yang)
no bitter taste - empty-heat (deficient yin)
feeling of heat
all day - full heat (excess yang)
in the afternoon or evening - empty-heat (deficient yin)
fever
high fever - full heat (excess yang)
low-grade fever in the afternoon - empty-heat (deficient yin)
mind
very restless & agitated - full heat (excess yang)
vague anxiety, fidgeting - empty-heat (deficient yin)
sleep
dream-disturbed, very restless - full heat (excess yang)
waking up frequently during the night - empty-heat (deficient yin)
skin
red-hot painful skin eruptions - full heat (excess yang)
scarlet-red, flat, painless skin eruptions - empty-heat (deficient yin)
treatment method
clear heat - full heat (excess yang)
nourish yin, clear empty-heat - empty-heat (deficient yin)
bleeding
profuse - full heat (excess yang)
slight - empty-heat (deficient yin)
-
complicated syndromes of heat and cold (heat above & cold below) symptoms:
heat above: thirst, irritability, sour regurgitation, bitter taste, heat sensation in the chest, frequent desire to vomit, mouth ulcers
cold below: abdominal pain alleviated by warmth, loose stools, borborygmus, and profuse-pale urine
transformation of cold and heat syndromes:
cold in exterior transforming to heat in interior.
exterior cold: fever with aversion to cold, no sweating, headache, stiff neck, aches throughout body. as it goes deeper into interior of body and turns into heat, cold signs subside, fever persists and other heat signs are present: irritability, thirst, and a yellow tongue coat.
heat transforming into cold: abrupt appearance of cold limbs, pallor, deep slow with pulse with high fever, thirst, irritability and a surging rapid pulse
true and false phenomena in cold and heat syndromes:
treat heat, false cold - heat in the interior, false cold on the exterior: cold limbs, thirst with a desire for cold drinks, burning sensation in the chest and abdomen, no aversion to cold, but aversion to heat, irritability, dry throat, foul breath, deep-yeelow and scanty urine; and a deep, forceful pulse.
true cold, false heat - cold in interior, false heat on the exterior: feverishness of the body, flushed face, thirst, wants to cover the body, drinks warm liquids to relieve the thirst, clear urine, loose stools; pale tongue with white coat; superficial pulse
-
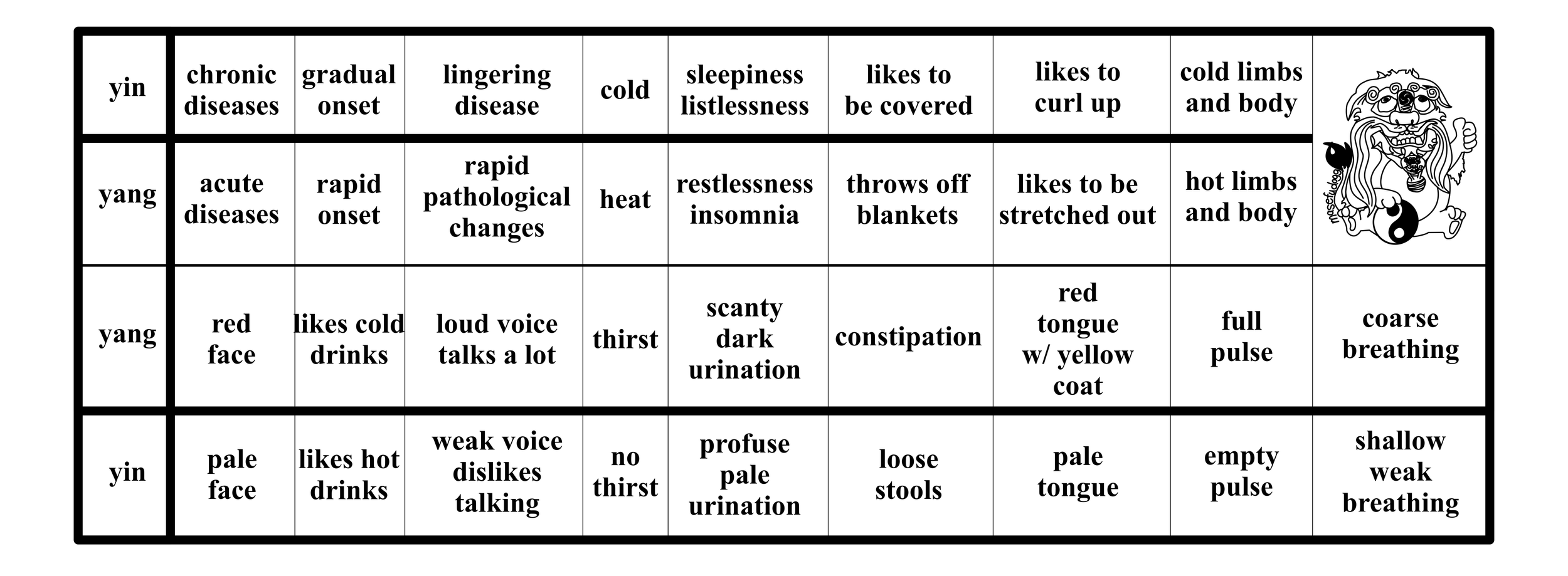
yang
any two or three of exterior, heat, excess
profuse perspiration with oily sweat
chilliness
cold limbs
no thirst
frequent profuse urine, or incontinence
loose stools or incontinence
weak breathing
minute, deep pulse
pale, wet, swollen and short tongue
yin
any two or three of interior, cold, deficient
notes:
when determining yang vs yin, remember it is the disease that is yang or yin, not a reflection of the patient's state of qi or yang/yin substances.
thus a "yang disease" is exterior, acute, sudden, excess, and hot.
a "yin disease" is interior, chronic, deficient and cold
collapse of yin:
abundant sticky perspiration
skin hot to the touch, warm hands and feet
hot limbs
dry mouth with desire to drink cold liquids in small sips
retention of urine
constipation
shortness of breath, restlessness
floating-empty & rapid pulse
red, peeled, short and dry tongue
zang fu diagnosis
-
DEFICIENCY
heart qi deficiency:
palpitations with qi deficiency signs: SOB, pale face, spontaneous sweating, fatigue, mild depression
tongue: pale
pulse: weak, thready
heart yang deficiency:
heart qi deficiency signs + feeling of cold, cold hands, discomfort in heart region
tongue: pale, swollen
pulse: deep, weak
yang collapse:
heart yang xu signs + cyanosis of lips, if severe may have coma, profuse sweat, feeble breathing
tongue: pale, bluish
pulse: hidden, minute, knotted
heart blood deficiency:
palpitations, insomnia, poor memory, dream disturbed sleep, anxiety, easily startled, pale lips and complexion
tongue: pale and thin
pulse: hesitant or thready
heart yin deficiency:
like heart blood deficiency, except more restlessness, dry mouth and thirst, night sweats, malar flush, feeling of heat
tongue: red, little coat
pulse: thready, rapid
EXCESS
heart fire blazing:
palpitations, agitation, thirst, tongue ulcers, feeling of heat, insomnia, dream disturbed sleep, red face, dark urine, bitter taste in morning
tongue: red, redder tip, swollen yellow coat
pulse: surging, rapid
phlegm misting the mind:
mental confusion, incoherent speech, rattling in throat, muttering to self quietly, lethargy, depression, aphasia, dull eyes, like the depressive phase of manic-depression
tongue: swollen, white sticky coat
pulse: rolling, string taut
phlegm fire harassing:
mental confusion, palpitations, thirst, bitter taste, rash behavior, chest oppression, rattling in throat, expectoration of phlegm, tendency to hit or scold, restlessness, uncontrolled laughter or crying, shouting, manic behavior
tongue: red, redder tip, yellow sticky coat, heart crack
pulse: rolling, rapid, forceful
heart qi stagnation:
palpitations with qi stagnation signs: chest oppression, slight SOB, depression, sighing, feeling of lump in throat, poor appetite, weak limbs, slightly purple lips, pale complexion
tongue: pale-purple
pulse: weak
heart vessel obstructed:
palpitations, SOB, inability to lie down, stabbing prickling pain in chest that comes and goes, may radiate shoulder/upper back, depression, restlessness, chest oppression, aggravated by cold, cold hands, purple lips
tongue: swollen with sticky coat, purplish spots
pulse: hesitant, string-taut or knotted
-
deficiency cold:
dull abdominal pain alleviated by pressure, desire for hot drinks, borborygmus, diarrhea, pale abundant urine, cold limbs
tongue: pale, white coat
pulse: deep, weak, slow
full heat:
restlessness, insomnia, heat in chest, tongue/mouth ulcers, dark scanty urine, burning upon urination, blood in urine, deafness
tongue: red, redder tip, yellow coat
pulse: surging, rapid
small intestine qi pain:
lower abdominal twisting pain, may extend to back, dislike pressure, borborygmus, flatulence, pain relieved by passing gas, pain in testes
tongue: white coat
pulse: surging, rapid
small intestine qi tied:
severe, sudden abdominal pain, dislike pressure, abdominal distention, constipation, vomiting, borborygmus, flatulence, similar to appendicitis
tongue: thick white coat
pulse: deep, string-taut
worms:
roundworms: abdominal pain, vomiting, cold limbs
hookworms: desire to eat strange objects
pinworms: itchy anus at night
tapeworm: constant hunger
-
DEFICIENCY & EXTERIOR PATTERNS
lung qi deficiency:
cough, SOB, weak voice, dislike speaking. spontaneous sweating, easy to catch colds, fatigue
tongue: pale
pulse: weak
lung dryness:
dry cough, dry skin or throat, hoarse voice, thirst
tongue: dry
pulse: weak
lung yin deficiency:
dry cough, weak hoarse voice, dry mouth/throat, possible blood streaked sputum, night sweats, dislike speaking, tiredness
tongue: red, little or no coat
pulse: thready, rapid
exterior wind cold
chills, fever, aversion to cold, itchy throat, clear watery discharge, sneezing, body aches, occipital HA, slight SOB
tongue: normal
pulse: superficial, tense
exterior wind heat
chills, fever, sore throat, thirst, yellow discharge, body aches, HA, slight sweat
tongue: normal, possible red sides
pulse: superficial, rapid
invasion wind water:
sudden swelling eyes/face, spread to body, shiny complexion, pale scanty urine, SOB, aversion to wind, fever, cough
tongue: sticky white coat
pulse: superficial, rolling
EXCESS PATTERNS
lung heat:
cough, slight sob, flaring nostrils, red face, thirst, feeling of heat
tongue: red, yellow coat
pulse: surging, rapid
damp phlegm:
chronic cough, SOB, white sticky phlegm easy to expectorate in morning, dislike lying down, nausea, wheezing, heaviness, muzziness, dizziness
tongue: swollen, sticky white coat
pulse: rolling, slow
heat phlegm
barking cough, SOB, yellow or green sputum, wheezing, chest oppression, feeling of heat, thirst, insomnia, agitation, heaviness, dizziness
tongue: red, swollen, sticky yellow coat
pulse: rolling, rapid
dry phlegm
dry cough, scanty difficult to expectorate sputum, SOB, chest oppression, heaviness, muzziness, dizziness, dry throat, wheezing
tongue: swollen, dry, sticky coat
pulse: rolling, thready
phlegm fluids
cough with white watery frothy sputum, SOB, splashing sound in chest, vomiting, chest oppression, heaviness, muzziness, dizziness
tongue: pale, sticky white coat
pulse: rolling, soft, or string taut
-
DEFICIENCY PATTERNY
large intestine dryness:
dry stools, difficult to pass, dry mouth and throat, foul breath, dizziness
tongue: dry, pale or red
pulse: thready
large intestine deficiency cold:
loose stools like duck droppings, dull abdominal pain, pale urine, borborygmus, cold limbs
tongue: pale
pulse: deep, weak
large intestine collapse
chronic diarrhea, prolapsed anus, hemorrhoids, tired after bm, cold limbs, desire for warm, desire for abdominal massage
tongue: pale
pulse: deep, weak, thready
LARGE INTESTINE EXCESS PATTERNS:
large intestine damp heat:
abdominal pain not relieved by bm, abdominal fullness, diarrhea, mucus and blood in stools, offensive odor, burning anus, dark urine, thirst no desire to drink, sweating does not reduce fever, heaviness body/limbs
tongue: red, sticky yellow coat
pulse: rolling, rapid
large intestine heat
constipation with dry stools, scanty dark urine, burning in anus, thirst, dry tongue, burning, sensation in mouth
tongue: thick dry yellow coat
pulse: excess, rapid
heat obstructing:
constipation, burning in anus, abdominal distention worse with pressure, high fever, tidal fever, sweating on limbs, vomiting, thirst, delirium
tongue: red, thick dry yellow coat
pulse: deep, excess
excess cold invading
sudden cramping abdominal pain, diarrhea with pain, feeling of cold, cold abdomen
tongue: thick white coat
pulse: deep, tense
large intestine qi stagnation:
constipation with bitty stool, irritability, abdominal distention and pain, condition aggravated according to mood
tongue: normal
pulse: string-taut
-
DEFICIENCY AND MIXED PATTERNS:
liver yin deficiency:
dizziness, numbness, tingling, blurry vision, ‘floaters’, dry eyes, poor night vision, scanty menses, amenorrhea, dull pale complexion, muscle weakness, cramps, withered nails, dry hair and skin, depression, yin deficiency: red cheekbones
tongue: red, without coat
pulse: thready, rapid
liver blood deficiency:
dizziness, numbness, tingling, blurry vision, ‘floaters’, dry eyes, poor night vision, scanty menses, amenorrhea, dull pale complexion, muscle weakness, cramps, withered nails, dry hair and skin, depression, yin deficiency: red cheekbones
tongue: pale, thin
pulse: thready
liver yang rising:
dizziness, tinnitus, HA, deafness, blurry vision, dry mouth/throat, insomnia, hypertension, irritability
tongue: red
pulse: string-taut
liver yang rising generating wind:
tremor, severe dizziness, tinnitus, HA, hypertension, dry eyes, blurry vision, numbness
tongue: red
pulse: string-taut
liver blood deficiency generating wind:
fine tremor, blurry vision, dizziness, numbness, scanty menses, insomnia, poor memory
tongue: pale, thin
pulse: string-taut, thready
extreme heat generating wind:
high fever, convulsions, stiff neck, opisthotonos, coma if severe
tongue: deep red, dry yellow coat
pulse: string-taut, rapid
EXCESS PATTERNS:
liver qi stagnation:
irritability, hypochondria fullness, pain, moodiness, sighing, depression, plum pit, irregular menses, PMS, breast distension
tongue: normal or dusky purple
puse: string-taut
rebellious liver qi
liver overact on stomach, nausea, vomiting, belching, hiccup, distention, irritability, breast distention
tongue: normal red sides
pulse: string-taut
liver fire
temporal headache, red face/eyes/nose bridge, thirst, bitter taste, easily angered, dream disturbed sleep, constipation, dark urine, epistaxis, hemoptysis
tongue: red, redder sides, dry yellow coat
pulse: string-taut, rapid
damp heat in liver
hypochondriac fullness, bitter sticky taste, poor appetite, nausea, feeling of heaviness, vaginal discharge, genital redness/itching, burning dark urination
tongue: red, redder sides, sticky yellow coat
pulse: rolling, string taut, rapid
liver blood stasis
hypochondria pain, abdominal masses, painful menses with clots, hemoptysis, epistaxis, purple nails
tongue: purple, possible with spots on sides
pulse: string taut
cold in liver channel:
hypochondria pain refer to scrotum, better with warmth, vertex HA, cold hands/feet, vomit, clear fluids
tongue: pale, wet white coat
pulse: deep, slow, string taut
-
gb deficiency:
dizziness, blurry vision, indecision, timidity, easily startled, lack of courage and initiative, wake up too early in the morning
tongue: pale
pulse: weak
damp in the gall bladder:
hypochondriac pain, fullness, jaundice, yellow sclera, feeling of heaviness, nausea, vomiting, dull headache, no thirst, sticky taste, turbid urination, inability to digest fats
tongue: sticky white coat bilateral two strips or one unilateral strip
pulse: rolling, string-taut
damp heat in gall bladder
hypochondriac pain, fullness, jaundice, yellow sclera, feeling of heaviness, nausea, vomiting, thirst no desire to drink, bitter taste, dizziness, irritability, swelling of feet, loose stool or constipation, dark urination, alternate hot and cold, feeling of heat, inability to digest fats
tongue: sticky yellow coat bilateral two strips or one unilateral strip
pulse: rolling, string-taut, rapid
-
DEFICIENCY PATTERNS
spleen qi deficiency:
poor appetite, abdominal distention, low energy, tired after eating, weak limbs, loose stools, pale face
tongue: pale
pulse: weak
spleen qi sinking:
spleen qi deficiency + bearing down sensation in abdominal, organ prolapse, frequent urination, chronic diarrhea, menorrhagia
tongue: pale
pulse: weak
spleen yang deficiency:
spleen qi deficiency + easy bruising, bleeding under skin, blood in urine or stools, excess uterine bleeding
tongue: pale
pulse: thready, weak
spleen blood deficiency
spleen qi deficiency signs; deficiency causes poor production of blood, scanty menses, insomnia, sallow complex
tongue: pale, thin
pulse: hesitant, thready
EXCESS PATTERNS
cold damp invading spleen:
poor appetite, fullness, heaviness, cold in abdominal, sweetish or lack of taste, loose stool, lassitude, tiredness, nausea, edema, excess white vaginal discharge, greenish color around mouth
tongue: pale, sticky white coat
pulse: rolling, slow or soft
damp heat invading spleen
poor appetite, fullness, heaviness, thirst no desire to drink, nausea, vomiting, loose stool with offensive odor, feeling of heat, dark urine, low-grade fever, sweating that does not lower fever, headache with feeling heaviness, skin eruptions
tongue: red, yellow sticky tongue coat
pulse: rolling, rapid or soft, rapid
-
DEFICIENCY PATTERNS
stomach qi deficiency:
uncomfortable feeling in epigastrium, no appetite, no taste, loose stools, weak limbs, tired especially in the morning
tongue: pale
pulse: weak right middle position
stomach yin deficiency:
hunger no desire to eat, dull burning pain epigastrium, constipation, dry mouth/throat, desire for small sips
tongue: red, geographic or no coat in center
pulse: thready, rapid
stomach deficiency cold:
dull pain in epigastrium better with eating or pressure, prefer warm food and drink, no appetite, vomit clear fluids, cold limbs, tired, pale face
tongue: pale, moist
pulse: slow
EXCESS PATTERNS
stomach qi stagnation:
epigastric pain, distention, nausea, vomiting, belching, hiccupping, irritability
tongue: normal
pulse: string taut right middle position
stomach fire:
burning epigastric pain, thirst for cold liquids, restlessness, bleeding gums, dry mouth, mouth ulcers, excess hunger, sour regurgitation, foul breath, feeling of heat, dry stool
tongue: red, dry yellow, possibly black coat
pulse: rapid
stomach phlegm fire:
stomach fire + oppression in chest, mucus in stools, expectoration of phlegm, mental derangement
tongue: red, sticky yellow coat
pulse: rolling, rapid
cold invading stomach
sudden severe pain in epigastrium, cold limbs, prefer warm, vomiting clear fluids, vomit after drinking
tongue: thick white coat
pulse: deep, tense, slow
stomach qi rebellion:
nausea, vomiting, belching, hiccupping, difficulty swallowing
tongue: normal
pulse: string-taut or tense right middle
damp heat in stomach
epigastric fullness, pain, heaviness, nausea, thirst no desire to drink, sticky taste, feeling of heat, thick nasal discharge
tongue: red, sticky yellow coat
pulse: rolling, rapid
food stagnation:
epigastric fullness, pain, distention, better with vomiting, nausea, sour regurgitation, belching, aversion to food, loose stool or constipation, excess dreaming
tongue: thick, sticky
pulse: rolling
blood stasis in stomach:
severe, stabbing epigastric pain, worse at night, dislike pressure, nausea, possible vomiting blood
tongue: purple
pulse: string-taut
-
DEFICIENCY PATTERNS
kidney yin deficiency:
dizziness, tinnitus, vertigo, poor hearing, poor memory, night sweats, dry mouth and throat, afternoon or evening fever, low backache, dark scanty urination, constipation, infertility, premature ejaculation, anxiety
tongue: red, little or no coat
pulse: thready, rapid
kidney yang deficiency:
low back pain, cold in lumbar and knees, feeling of cold, weak legs, abundant clear urination, urination at night, edema lower legs, loose stools, impotence, infertility, decreased libido, low sperm count, lassitude
tongue: pale, white coat
pulse: deep, weak, slow
kidney qi not firm:
sore low back, weak knees, frequency copious urine, dribbling after urination, incontinence, enuresis, nocturnal emission without dreams, premature ejaculation, spermatorrhea, vaginal discharge, bearing down sensation, recurring miscarriage
tongue: pale, white coat
pulse: thready, weak
kidney failing to receive qi
SOB with exertion, rapid weak breathing, chronic cough, asthma, spontaneous sweating, low backache
tongue: pale
pulse: deep, weak, tense
kidney jing deficiency
in children: poor development, growth/mental retardation, fontanelles not closed
in adults: premature aging, early loss teeth/hair, infertility, soft bones, memory loss
tongue: like yin or yang deficiency, whichever is more evident
pulse: thready, rapid, or deep, weak
COMBINED PATTERNS
kidney yin deficiency with empty heat blazing:
malar flush, night sweats, insomnia, afternoon/evening fever, 5-palm heat, dry throat, thirst for small sips, dizziness, tinnitus, low back pain, nocturnal emission with dreams, excess sexual desire, dark urine
tongue: red, cracked with red tip, no coat
pulse: thready, rapid
kidney yang deficiency with water overflowing:
edema lower legs, feeling of cold in low back, abdominal distention/fullness, clear scanty urination, possible palpitations, SOB, frothy sputum, cold hands, cough, asthma
tongue: pale, swollen, moist white coat
pulse: deep, weak, slow
-
bladder deficient cold:
frequent pale abundant urination, incontinence, enuresis, cold low back, feeling of cold
tongue: pale, moist
pulse: deep, weak
damp heat in urinary bladder:
frequent, urgent, difficult urination with burning sensation, dark in color, possibly blood in urine, thirst no desire to drink, feeling of heat
tongue: thick, sticky yellow coat at root
pulse: rolling, rapid
cold damp in urinary bladder:
frequent, urgent, difficult urination, often stopping midstream, feeling of heaviness in hypogastrium and urethra, pale and turbid in color
tongue: white sticky coat at root
pulse: rolling, slow
-
DEFICIENCY PATTERN
blood deficiency:
heart blood deficiency symptoms plus chest discomfort, tightness, dull ache and slight SOB
tongue: pale, thin, slightly dry
pulse: hesitant, thready
EXCESS PATTERNS
heat in pericardium by an external pathogen:
mental confusion, delirium, incoherent speech, fever at night, obvious macules, like ying or blood level heat
tongue: red, dry, no coat
pulse: thready, rapid
pericardium fire:
like heart fire plus tightness, heat and slight ache in the chest, rapid breathing
tongue: red, redder on tip, swollen with red points, yellow coat, possibly midline crack to the tip
pulse: excess, rapid or abrupt
phlegm fire harassing pericardium:
phlegm fire harassing heart with heat sensation in chest, chest oppression, rapid breathing
tongue: red, redder on tip, swollen with red points, yellow dry sticky coat, deep midline crack
pulse: excess, rapid, rolling or excess, rapid, string-taut
qi or blood stagnation in pericardium:
same as heart qi or blood stagnation
six-stages/shang han lun
-
first described by dr. zhang zhong-jing around 200 ad in the text shang han za bing lun;
it was later edited into the shang han lun and jin kui yao lue (golden cabinets).
the focus is diseased, started by cold pathogens.
-
chills and fever, aversion to cold, head/neck stiffness and pain, superficial pulse
taiyang channel excess: more cold, no sweating, pulse also tense -
ma huang tang, ge gen tang
taiyang channel deficiency: more wind, patient has sweating, pulse also moderate -
gui zhi tang
taiyang fu water accumulation: aversion to cold, urinary retention, vomiting immediately after drinking -
wu ling san
taiyang fu blood accumulation: lower jiao distention, fullness, urgency, blood in urine, restlessness -
tao he cheng qi tang
-
fever, sweating, aversion to heat
yangming jing: high fever, profuse sweat over entire body, thirst for cold water, big pulse, (4 bigs), red tongue, white or yellow dry coat
bai hu tang
yangming fu: tidal fever, sweating on hands and feet, constipation, fullness, red tongue, dry yellow coat, rolling, rapid pulse
da cheng qi tang
xiao cheng qi tang
tiao wei cheng qi tang
-
bitter taste in mouth, dry throat, dizziness, blurry vision, alternating chills and fever, fullness in chest and hypochondrium, low appetite, normal tongue, string-taut pulse
xiao chai hu tang
-
interior deficient cold, abdominal fullness, sometimes pain, reduced appetite, no thirst, loose stool, diarrhea, fatigue, edema, pale tongue with white coat, deep, weak pulse
though taiyin includes lu/sp, taiyin channel symptoms related to mostly spleen
li zhong wan
-
heart and kidney, affecting shen
shaoyin cold: aversion to cold, listlessness, desire to sleep, lying with body curled up, diarrhea, frequent pale urination, pale tongue, white coat, deep weak pulse
si ni tang
zhen wu tang
shaoyin heat: irritability, insomnia, dry mouth, dry throat, night sweats, dark urine, red tongue little coat, thready, rapid pulse
huang lian e jiao tang
-
mix heat and cold, heat above and cold below, heat and irritability in chest, energy rising in chest, thirst, diarrhea, vomiting, cold limbs, possible roundworms, pale tongue, white coat, deep, slow pulse
wu zhu yu tang
si ni san
wu mei wan
four-levels/wen bing
-
first described in the 1600’s in response to acute exogenous febrile diseases
i.e. epidemic diseases. the illness is characterized by high fever damaging yin, quick progression, easy to cause movement of blood
-
fever, slight chills, headache, cough, thirst, dry mouth, yellow nasal discharge, normal tongue or red tip, superficial, rapid pulse
exterior heat
-
high fever, aversion to heat, sweating, thirst, dry mouth, irritability, cough with yellow sputum, scanty urine, constipation, red tongue, dry yellow coat, surging, rapid pulse
organ level heat
-
fever worse at night, thirst no desire to drink, dry mouth, irritability, insomnia, delirium, restlessness, skin rashes, very red tongue, little or no coat, rapid thready or choppy pulse
nutritive level heat
-
like ying level heat, but more severe, fever worse at night, thirst no desire to drink, dry mouth, irritability, insomnia, delirium, convulsions, loss of consciousness, obvious bleeding, red tongue, little coat, thready rapid pulse
blood level heat
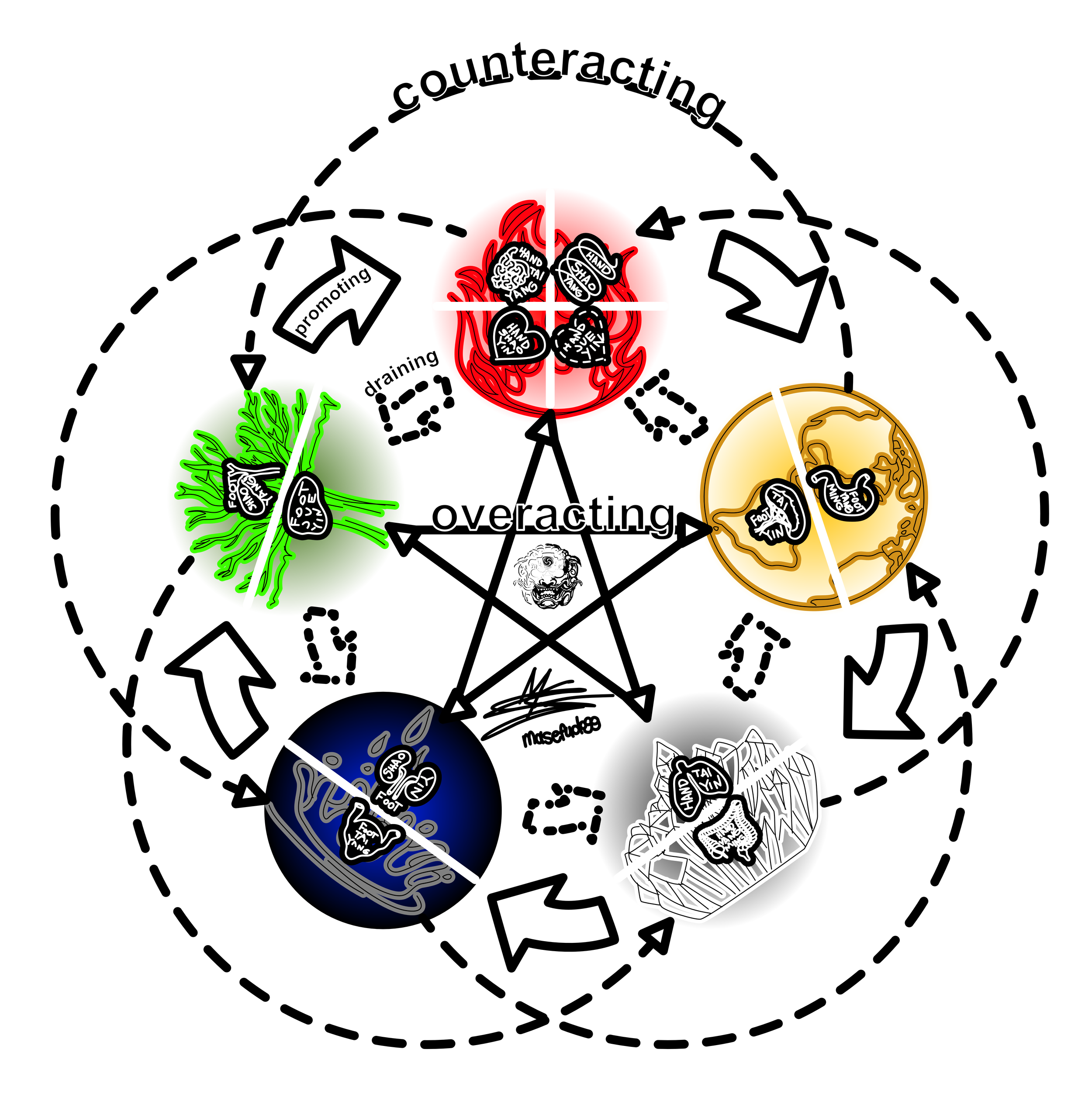
five element relationships
-
wood promotes fire
fire promotes earth
earth promotes metal
metal promotes water
water promotes wood
-
same relationship between organs as control cycle, now signifying a pathological condition
normal mechanism for organs to keep each other in balance
wood controls earth
earth controls water
water controls fire
fire controls metal
metal controls wood
wood overacting earth: wood creating rebellious qi (hypochondriac pain, irritability, nausea, diarrhea)
fire overacting metal: fire dries up lung fluids (cough, yellow sputum)
earth overacting water: spleen damp (disturbance in fluid excretion, edema)
metal overacting wood: lung qi obstruct (fatigue, irritability, liver qi stagnation)
water overacting fire: kidney yin xu (xu heat in heart - some texts say kidney can’t overact)
-
same organ relationship as control cycle, but opposite direction; also pathological
wood counteracting metal: obstructed qi (breathlessness, paroxysmal cough)
fire counteracting water: heat drying fluids (kidney yin xu, night sweats, malar flush, insomnia)
earth counteracting wood: spleen damp impedes liver qi (hypochondriac distention, jaundice
metal counteracting fire: phlegm in lung impairs heart blood circulation (palpitations, insomnia)
water insulting earth: kidney not transforming fluid (spleen damp, loose stools, edema, fatigue)
-
wood not nourishing fire: liver blood not nourishing heart blood (insomnia, palpitations, timidity)
fire not nourishing earth: heart shen is needed for spleen yi concentration (distracted thinking)
earth not nourishing metal: spleen not transforming (phlegm in the lung)
metal not nourishing water: lung qi not sending qi and fluids down (breathlessness, asthma, dryness)
water not nourishing wood: kidney not supplying yin to liver (liver yin a/o blood xu, tinnitus, dizziness, headache, irritability)
-
wood being drained by fire: heart blood xu causing general blood xu (scanty menses, amenorrhea)
fire being drained by earth: spleen not making enough blood (palpitations, insomnia, poor memory, depression)
earth being drained by metal: xu lung qi (general qi xu, fatigue, loose stools, no appetite)
metal being drained by water: deficient kidney not grasping qi (breathlessness)
water being drained by wood: long term liver blood xu (kidney essence xu, night sweats, dizziness, tinnitus
-
wood:
green complexion
small head
straight back
tall, slender
strong bones
small hands/feet
fire:
red complexion
small pointed head
curly hair
small hands
walks fast
earth:
yellow complexion
round face
large head
large abdomen
strong thighs
metal:
white complexion
square face
flat abdomen
strong body
strong voice
walks slow
water:
dark complexion
broad face
large head
large abdomen
long spine
san jiao differentiation
-
created in response to heat patterns around 1800
focuses on the region of the body and the organs attacked
-
lung: fever aversion to wind and cold, thirst, sore throat, cough, chest pain or oppression, red tongue, yellow coat
like wen bing wei or qi level
-
stomach or intestines: dry heat causing red face, red eyes, high fever, thirst, dry throat, nausea, vomiting, constipation, red tongue, dry coat, thready rapid pulse
similar to yangming jing, yangming fu, or wen bing qi level
spleen: damp heat in spleen causing fullness in epigastrium, no appetite, heavy limbs, diarrhea, greasy tongue coat, rolling rapid pulse
similar to wen bing qi level
-
kidney: low-grade fever in afternoon or evening, five center heat, dry mouth and throat, night sweats, deafness, insomnia, lassitude, deep red tongue, no coat, thready rapid pulse
like shaoyin heat
liver: fever, coma, convulsions, tremors, dizziness, dream disturbed sleep, deep red tongue, no coat, thready, rapid or thready, rapid, wiry pulse
similar to wen bing blood level
-
fever, thirst, desire for cold water, burning and pain in whole body, irritability, dark scanty urine, constipation, red tongue, yellow coat, rolling rapid pulse
inspection of the body
-
falling out: blood deficiency
prematurely gray: decline of kidney essence
state of the hair: blood or kidney essence
thickness and luster of the hair: dependant on the liver
dull hair with a tendency to split: deficiency of liver blood
-
lustrous & moist complexion
disease is mild, qi and blood are not deficient, prognosis is good.
dark & haggard complexion
disease is severe, essential qi is already injured, prognosis poor
clear and rather moist
stomach qi good. dry and rather lifeless - stomach qi is exhausted
green color
interior cold, pain, or interior wind (liver pattern)
deep color - interior. floating color - exterior
clear color - yang condition.
dull color - yin condition
thin color - qi deficiency
thick color - full condition
scattered color - new disease
concentrated color - old disease
red
entire face - excess heat syndrome from exogenous pathogen, or hyperactive yang
malar flush with tidal fever and night sweating - interior heat d/t yin def.
pale
cold syndromes of deficiency type, and loss of blood
pale complexion is often due to yin excess or yang deficiency
bright white face with puffy, bloated appearance - sign of deficiency of yang qi
pale, withered face - blood deficiency
yellow
deficiency and damp ype syndormes
entire body is yellow - jaundice
tends toward bright orange - yang jaundice from damp heat
hazy and smoky yellow - yang jaundice with more damp than heat
withered, dried up yellow - heat in stomach and spleen
sallow yellow - deficiency of stomach and spleen
dull pale yellow - cold damp in stomach and spleen
pale yellow without brightness - deficiency of both qi and blood
pale with red spots - spleen deficiency, and stasis of liver blood
clear & moist between eyebrows - stomach qi is recovering after a long illness
smoky, dark yellow - yin jaundice from cold-damp or long-standing blood stagnation
blue
cold, pain, blood stagnation, and/or convulsions.
pale and blue - excess yin and cold, with severe pain in epigastrium and abdomen
bluish-purple face and lips:
with intermittent pain in precordial region or behind the sternum - stagnation of heart blood
with high fever, violent movement of limbs in children - signs of infantile convulsions
dark-bluish complexion - cold or chronic pain
dull-blue complexion - severe yang deficiency with blood stasis or chronic pain
bluish complexion in children - liver wind
green
pale green under the eyes - liver qi stagnation
green complexion on cheeks - liver qi stagnation, liver blood stasis, cold in liver, liver wind
green with a red tinge - lesser yang pattern
green color with red eyes - liver fire
yellowish green cheeks - phlegm with liver yang rising
green color on nose - stagnation of qi with abdominal pain
dark reddish green - stagnant liver qi turning into heat
pale green under the eyes - liver blood deficiency
dark gray
kidney deficiency and blood stagnation
pale and dark complexion, with lumbar soreness and cold feet - insufficient kidney yang
dark color complexion without brightness, but with scaly skin - prolonged blood stagnation
white
deficiency or cold - blood deficiency or yang deficiency
black
cold, pain, or kidney disease - kidney yin deficiency
black and moist looking - cold
dried up and burnt - heat from kidney yin deficiency
-
red tip of nose - spleen deficiency
bluish color in the center of the forehead - heart has suffered shock
short chin - kidney deficiency
-
red color in corner of eye - heart fire
red color in sclera - lung heat
green, blue, purple, or red spots appearing at the end of red veins, with purple blood spots on them - lesions in back or chest. if spots are not connected to veins, they have no diagnositc significance.
gray and scattered spots, like clouds - injury of qi
deep black spots, like sesame seeds - injury of blood
black spots surrounded by a gray cloud-like halo - injury of qi & blood
red veins visible and spiral shaped - pain
upward, straight forward or sideways staring of eye - disturbance of liver wind
yellow color in the sclera - damp heat jaundice
dull white color in the corners of the eye - heat
-
slightly moist and shiny - disease not serious
dry - heat in stomach in li
dry and black - presence of fire poison
flapping of the ala nasi sometimes in asthmatic breathing - d/t lung heat, lung & kidney qi deficiency deficiency
clear nasal discharge - exposure to cold
turbid discharge - exposure to wind-heat
prolonged turbid nasal discharge with stinky smell - chronic rhinitis, or chronic sinusitis
tip of the nose is green or blue - abdominal pain
tip of the nose is yellow - damp heat
white color - blood deficiency
red color - heat in the lungs and spleen
gray - impairment of water movement
-
dry & withered auricles, burnt-black in color - prolonged or severe illness, due to consumption of kidney essence, or due to kidney qi deficiency
lobes are dry, withered and black - extreme exhaustion of kidney qi
purulent discharge "tin ear" (infection) - damp heat of the liver & gall bladder
white color - cold pattern
bluish or black color - pain
long and full lobe - strong kidneys and good constitution
thin and small lobe - poor constitution
swelling and pain of ear or middle ear - fire in the shao yang channels
thin ear - deficiency of qi and blood
-
teeth are an extension of the bones, influenced by the kidneys
teeth are bright and dry, like a stone - heat in yang ming in context of exterior diseases
teeth are dry and grayish - kidney yin deficiency
gums are under the influence of the stomach
pale gums - blood deficiency
redness and swelling of gums & teeth - flaring of stomach fire, if no pain - empty heat
redness and swelling with bleeding - injury of the vessels by stomach fire
-
blood deficiency, very pale lips - blood or yang deficiency
-
bluish-purple lips - retention of cold or stagnation of blood
dry lips, deep red in color - excessive ehat, heat in the spleen & stomach
mouth always slightly open - deficiency
only breathes through mouth - lung qi deficiency
sudden collapse with open mouth - deficiency.
sudden collapse with locked jaw - excess
greenish color around the mouth - liver blood stasis & invasion of the spleen by liver qi
-
red and swollen with yellow or white ulcer spots - excess toxic-heat in the lung and stomach
bright red with mild soreness - yin deficiency leading to hyperactivity of fire
false membrane over throat, grayish white, hard to remove, bleeding after forceful rubbing, returns immediate - diphtheria from heat in lung consuming yin.
-
swollen tonsils normal color - retention of dampness or phlegm from qi deficiency most often seen in children recovering from pathogenic factors and chronic upper respiratory infections.
chronic redness & swelling that comes and goes - chronic heat in st, li and more common children
red and swollen tonsils with exudate - wind heat and or toxic heat in st, li
greyish tonsils - acute glandular fever (mononucleosis)
-
healthy color & firmness of the flesh around ankles & wrists - good state of body fluids
skin lacks luster & is dry, the flesh is shriveled - exhaustion of body fluids
pale nails - blood deficiency
bluish nails - liver blood stasis
bluish color venules on the thenar eminence of the thumb - cold in the stomach
bluish and short venules - deficiency pattern
red venules - heat in the stomach
rigid - liver yang rising or liver wind in elderly, bi syndrome with dampness
empty conditions - liver deficiency & kidney yin, spleen or kidney yang (more common elderly)
limb paralysis - usually d/t spleen & stomach deficiency, or qi and blood deficiency, yin deficiency of liver and kidneys
full conditions - retention of dampness in muscles and blood stasis
contraction of limbs - acute - wind empty - liver blood or liver yin deficiency
limb tremors - wind, & or liver wind, phlegm, liver yang rising, liver blood deficiency, liver and kidney yin deficiency
-
index fingers of children under two are used for diagnosis
left finger in boys and right finger in girls
the creases on the fingers are called "gates", if venules appear beyond the gate
first gate, gate of wind (base of finger/mcp) - exterior pathogen/mild disease
second gate, gate of qi (pip) - interior/more severe disease
third gate, gate of life (dip) - serious/life threatening disease
blue venules - cold
red venules - heat
-
thin person with dry skin - insufficiency of blood
thin and emaciated person - long-term deficiency of blood and yin
overweight with mental depression - deficiency of qi and excess phlegm damp
great loss of weight in the course of a long illness -exhaustion of essential qi
sit facing downward and dislikes speaking - may indicate qi deficiency with sob
violent movement of the four limbs - wind diseases (tetanus, infantile convulsions)
wei syndrome - weakness, motor impairment, muscular atrophy of the limbs
bi syndrome - numbness, pain, heaviness in the tendons, bones and muscles accompanied by swelling and restricted movements of the joints
numbness & impaired movements of limbs on one side of body - hemiplegia or wind stroke
wood types - a tall, slender body
metal type - broad, square shoulders, strongly built body, triangular face; moves slowly and deliberately. if they move quickly, there is a problem.
earth type - slightly fat body; large head, belly, & thighs; wide jaws
water type - round face and body, with a long spine
fire type - pointed head, small hands, moves quickly. if they move slowly, there is a problem
person moves quickly & throws off the bed covers - may indicate liver or heart problems
small movements & continuous fidgeting, especially of the legs - deficiency heat pattern of the kidneys.
-
skin is related to liver (through the blood), lungs, and stomach (heat)
dry skin - liver blood deficiency. itching skin - wind
swelling of skin, leaves a fingermark with pressure - true (water) edema d/t kidney yang deficiency
the questions to ask
-
aversion to cold/chilly - external invasion of w/c or w/h (d/t pathogenic factor blocking defensive qi).
low grade fever, worse in the afternoon or only in the afternoon - yin deficiency.
constant low-grade fever - damp heat.
fever in the middle of the night: in adults - yin deficiency; in children - retention of food.
alternating chills & fever - symptom of intermediate syndromes
-
area of body
only on head - heat in stomach or damp heat
only arms and legs - stomach and spleen deficiency
only on hands - lung qi deficiency, heart qi deficiency
whole body - lung qi deficiency
palms, soles, and chest - yin deficiency
(oily sweat) on forehead - yang collapse
time of day:
during the day - yang deficiency
during the night - yin deficiency (in some cases, it may be d/t damp heat)
condition of illness:
profuse, cold sweat during a severe illness - yang collapse
oily sweat on forehead, like pearls, not flowing - yang collapse (danger of imminent death)
quality of sweat:
oily - severe yang deficiency
sticky collapse of yin
yellow - damp heat
-
headache onset:
recent onset, short duration - external wind cold attack
gradual onset - internal condition
headache time of day:
daytime - qi or yang deficiency
evening - blood or yin deficiency
nighttime-blood stasis
headache location:
nape of neck - tai yang channels (exterior wind-cold or kidney deficiency)
forehead - yang ming channels (stomach heat or blood deficiency)
temples or sides - shao yang channels (exterior w-c or w-h, or interior lv & gv fire rising)
vertex jue yin channels (liver blood deficiency)
whole head - exterior wind cold
headache character of pain:
heavy feeling - dampness or phlegm
pain "inside" the head, "hurting the brain" - kd deficiency
distending, throbbing - lv yang rising
boring, like a nail - blood stasis
feeling of muzziness, heaviness - damp add dizzziness and it becomes phlegm
feeling of muzziness, heaviness, dizziness - phlegm
occipital headache and stiffness - external wind
headache condition:
occurs with aversion to wind or cold - external invasion
aggravated by cold - cold pattern
aggravated by heat - heat pattern
aggravated by fatigue, improved by rest - qi deficiency
aggravated by emotion tension - liver yang rising
aggravated by sexual anxiety - kidney deficiency
dizziness:
severe giddiness, everything seems. tosway, person loses balance - internal wind
slight dizziness with heaviness & muzziness of head - phlegm (prevents clear yang rising to head)
slight dizziness aggravated when tired - blood deficiency
sudden onset of dizziness - full pattern, gradual onset of dizziness - empty pattern
dizziness with throbbing headaches - liver yang rising
nose
chronic profuse runny nose with clear watery discharge - lung qi deficiency or yang deficiency of lung & kidney and du mai
dryness with throbbing headache - liver yang rising
bridge green - liver qi stagnation, bridge grayish or dark - liver blood stasis, red - liver fire
nose slightly moist and shiny - good prognosis
dry nose - heat in stomach or large intestine
mouth ulcers
very painful, red-rimmed on gums - stomach full heat
pale-rimmed on gums - stomach empty heat
tip of tongue - heart fire or heart deficiency
insides of cheeks - stomach heat
during pregnancy - disharmony of directing vessel
pale rimmed aggravated by overwork - kidney yin deficiency or original qi deficiency
ulcers that come and go - empty condition - or ulcers that are frequent - full conditions
bleeding gums
poor appetite, bleeding gums, loose stools, tiredness - spleen qi deficiency (not hold blood)
bleeding gums, thirst, heat - stomach full heat
bleeding gums, dry mouth, desire to drink small sips - stomach yin deficiency
bleeding gums, dizziness, tinnitus, night sweating, malar flush - kidney yin deficiency
-
pain in whole body
sudden onset, with chills and fever - external wind-cold
occipital headache with stiffness - external wind
pain all over with tiredness - qi and blood deficiency
in woman after childbirth: dull pain - blood deficiency, severe pain - blood stasis
pain in arms and shoulders only when walking - liver qi stagnation
pain in all muscless with hot sensation in the flesh - stomach heat
pain with feeling of heaviness - dampness obstructing the muscles
distening/bloating more than pain or no fixed location - qi stagnation
chronic headaches with distending, throbbing pain - liver yang rising
severe boring or stabbing with fixed location - blood stasis
intense pain with feeling of fullness (more children) - retention of food
pain in joints
wandering from joint to joint - wind
fixed and very painful - cold
fixed with swelling and numbness - dampness
fixed with swelling and redness of the joints - damp-heat
severe stabbing pain with rigidity - blood stasis
rheumatoid arthritis - phlegm
pain in joints or epigastrium - external dampness
backache
continuous, dull - kidney deficiency
recent onset, severe, with stiffness - sprain of back, causing blood stasis
severe pain, aggravated by cold/damp weather, alleviated by heat - external cold & damp to back channels
boring pain with inability to turn the waist - blood stasis
pain in back extending up to shoulders - external attack wind
numbness
numbness of arms & legs, or only hands & feet on both sides - blood deficiency
numbness of fingers, elbow & arm on one side only (especially first 3 fingers) - interior phlegm & wind (this may indicate the possibility of impending wind stroke)
cold hands
yang deficiency, (usually), blood deficiency, or qi stagnation
palpitations & dizziness - heart blood deficiency
weak knees
kidney yang deficiency
cold feet
kidney yang deficiency (usually), in women liver blood deficiency
-
chest
thorax influenced by - heart, lungs
flanks influenced by - liver, gall bladder
pain in chest - blood stasis in heart, which is usually d/t yang deficiency
pain in chest accompanied by cough with profuse yellow sputum - lung heat
feeling of oppression - phlegm in lungs, severe liver qi stagnation
hypochondrium
feeling of distension - liver qi stagnation
stabbing pain - liver blood stasis
distention & stuffiness of hypochondrium - liver qi stagnation; with severe pain - liver blood stasis
epigastrium
dull pain in the epigastrium, not very severe - deficiency of cold in stomach
epigastric pain alleviated by eating - empty pattern
epigastric pain aggravated by eating - full pattern
fullness in epigastrium - spleen deficiency or dampness
feeling of distention - liver qi stagnation
abdomen
abdomen influenced by - liver, spleen, kidneys, bladder, intestines
lower abdominal pain - interior cold, liver qi or blood stagnation, damp heat, or blood stasis in uterus or intestines
differentiation based on accompanying signs & symptoms
abdomen pain relieved by bowel movements - full pattern
abdomen pain aggravated by bowel movements - empty pattern
hypogastrium pain
damp heat in urinary bladder or sometimes liver fire infusing downwards to the ub
-
food
relieved by eating - empty pattern; aggravated by eating - full pattern
lack of appetite - spleen qi deficiency, always hungry - stomach heat
hunger with no desire to eat or eating small amounts of food - stomach yin deficiency
fullness and distention after eating - food retention or damp, distention only - qi stagnation
preference for hot foods - cold pattern; preference for cold foods - heat pattern
sharp pain - blood stasis
taste
bitter taste - liver or heart full heat
constant bitter taste - liver fire
with insomnia & only present in morning after a sleepless night, not after a restful night - heart fire
sweet - spleen deficiency, or damp heat in the spleen
sour - food retention or liver-stomach disharmony
salty - kidney yin deficiency
pungent - lung heat
lack of taste - spleen & stomach deficiency
vomit
sour vomit - invasion of stomach by liver
bitter vomit - liver and gb heat
clear, watery vomit - cold in stomach with retention of fluids
vomit soon after eating - heat pattern
sudden and loud vomiting - full pattern
slow emission with a weak noise - empty pattern
-
constipation
worse after bowel movement - empty pattern; better after bowel movement - full pattern
acute constipation with thirst & a dry yellow tongue coating - stomach heat, or small intestine heat
constipation in the elderly or in postpartum women - blood deficiency
constipation with small, bitty stools like a goat's - liver qi stagnation and heat in the intestines
constipation with abdominal pain - internal cold and yang deficiency
constipation with dry stools, dry mouth, small sips - yin deficiency (usually of kidney &/or stomach)
stools not dry, but difficult to pass - liver qi stagnation
alternate constipation and diarrhea - liver qi stagnation invading the spleen
diarrhea
loose stools with undigested food - spleen qi deficiency
patient cannot hold their stools easily - central qi deficiency with sinking of spleen
diarrhea with abdominal pain and fullness, undigested food - interior cold in the intestines
black or very dark stools - stasis of blood
diarrhea with mucus in the stools - dampness in the intestines
diarrhea with mucus and blood in the stools, blood comes first, bright red, splashing in all directions - damp heat in the intestines
blood comes first, is turbid and the anus feels heavy and painful - heat in the blood
stools come first and then watery blood - spleen qi deficiency unable to hold blood
pain accompanying diarrhea - liver involvement or heat
burning sensation in the anus while passing stools or foul smelling stools - heat
borborygmus with loose stools - spleen deficiency
borborygmus with abdominal distension and without loose stools - liver qi stagnation
flatulence with foul smell - damp heat in the spleen or heat in the intestines
flatulence without smell - interior cold from spleen yang deficiency
-
function?
enuresis or incontinence - kidney deficiency
retention of urine - damp heat in urinary bladder
difficulty urinating - urinary bladder damp heat or kidney deficiency (especially in the elderly)
very frequent and copious urination - kidney deficiency
frequent and scanty urination - qi deficiency
pain?
pain before urination - qi stagnation in lower burner
pain during urination - heat in the ub
pain after urination - qi deficiency
color?
pale - cold pattern (usually ub and kd)
red or yellow or dark - heat
turbid or cloudy - damp in the ub
copious, clear and pale during w-c or w-h attack - pathogenic factor has not penetrated interior
dark urine during exterior invasion of w/c or w/h - pathogenic factor in the interior
dark urination during an exterior attack of w/h or w/c - pathogenic factor in the interior
-
insomnia
not being able to fall asleep, but sleeping well after falling asleep - heart, spleen, liver blood deficiency
waking many times - kidney, heart, liver yin deficiency
insomnia with anxiety, dream - disturbed sleep and qi and blood deficiency - heart and spleen blood deficiency
insomnia with difficulty in falling asleep, dizziness, blurred vision - liver blood deficiency
insomnia, waking up frequently during the night with excessive dreams together with night sweating and palpitations: heart & kidney yin deficiency with empty heat
dream-disturbed sleep - liver fire eor heart fire
restless sleep with dreams - food retention
wake up early in the morning and failing to fall asleep again - gall bladder deficiency
as we grow older, it's normal to wake early, d/t the physiological decline of qi & blood
lethargy
feeling sleepy after eating - spleen qi deficiency
lethargy and heaviness of the body - dampness
lethargy and dizziness - phlegm
extreme lethargy and lassitude with feeling of cold - kidney yang deficiency
lethargic stupor with exterior heat symptoms - invasion of pc by heat
lethargic stupor with rattling in throat, slippery pulse, sticky tongue coat - phlegm blurring the mind
-
tinnitus
sudden onset - full pattern (liver fire or liver wind)
gradual onset - empty pattern (usually a kidney deficiency)
aggravated by pressing hands over the ears - full pattern
alleviated by pressing hands over the ears - empty pattern
loud, high-pitched noise, like a whistle - liver yang, liver fire, or liver wind rising
low-pitched noise, like rushing water - kidney deficiency
deafness
sudden onset onset - full pattern (liver fire or liver wind)
gradual onset - empty pattern (usually kidney deficiency)
chronic deafness - kidney deficiency, heart blood deficiency, upper burner qi deficiency, yang qi deficiency
eye pain
pain like a needle, with redness of eye and headache - fire poison in heart channel
pain, swelling, & redness of eye - invasion of eye channels by exterior w/h or interior liver fire
blurry vision and floaters in the eyes - liver blood deficiency, liver yin or kidney yin deficiency
photophobia - liver blood deficiency, liver yang rising
pressure in the eyes -kidney yin deficiency
eye dryness
dry eyes - liver and/or kidney yin deficiency
eye observation
yellow sclera - jaundice
ulceration of the canthus - damp heat
upward, straight forward, or sideways staring of the eye - liver wind
dull white corners of the eyes - heat
pale white corners of the eyes - blood deficiency
swelling under the eyes - kidney deficiency
-
thirst with desire to drink large amounts of cold water: full heat pattern of any organ’
absence of thirst: cold pattern, usually spleen or stomach
thirst with no desire to drink: damp heat
thirst with desire to sip liquids slowly, or to sip warm liquids: yin deficiency (usually of stomach or kidney)
thirst for cold liquids: heat pattern; thirst for warm liquids - cold pattern
-
chronic tiredness, loose stools: spleen qi deficiency with cold signs - spleen yang deficiency
chronic tiredness, weak voice, easily catches colds: lung qi deficiency - with cold - lung yang deficiency
chronic tiredness, backache, lassitude, cold, depression, frequent urination: kidney yang deficiency
chronic tiredness, anxiety, tenseness, wiry pulse: liver qi stagnation
short-term tiredness, alternating cold & heat sensation, irritability, unilateral tongue coating: lesser yang
chronic tiredness with slight depression, dizziness and scanty periods: liver blood deficiency
-
distending pain in the chest, epigastric, hypochondriac, and abdominal regions: moving qi stagnation
prickling pain, boring, sharp and fixed: blood stagnation
weighty pain, heavy sensation: damp blocking qi and blood
colicky pain: abrupt qi obstruction by substantial pathogenic factors
pulling pain, spasmodic, and short: disorders of the liver caused by liver wind
burning pain, desires coolness: invasion of collaterals or lack of warmth in zang fu organs d/t yang qi deficiency
hollow pain: deficiency of blood
-
(don’t differ much from adults;
questions need to be asked in the presence of the parents)
consider the following:
nutritional, emotional, and physical state of mother during pregnancy; traumas at birth; breast-feeding and early weaning; vaccinations; childhood diseases contracted.
disturbed sleep in older children: liver fire, stomach heat, retention of food
weaning too early: can lead to retention of food and some skin diseases
too early weaning or rich food consumed too early: can lead to sore throats and/or runny nose
traumas at birth (such as caesarian or very long birth): affects baby’s lungs
whooping cough during childhood: weakens lungs especially if occurs in severe form
immunization: skin rash, insomnia, change in character - latent heat that could last to adulthood
chronic catarrh, constant runny nose, cough, glue ear: residual wind with a spleen deficiency and phlegm
chronic earache: lingering pathogenic factors usually damp-heat in gall bladder channel
chronic cough/wheezing/respiratory infections: lingering pathogenic factor, lung phlegm heat
-
impotence
young men - more a heart pattern rather than kidney deficiency
older men - kidney yang deficiency or kidney qi deficiency
heaviness of scrotum, urethral discharge, sticky yellow tongue - damp heat in liver
lack of libido
kidney qi or yang deficiency sometimes spleen, heart, lungs (most common heart)
premature ejaculation
kidney qi not firm, possible heart qi or heart blood deficiency
tiredness & dizziness after ejaculation
kidney deficiency
-
sexual
lack of libido - inability for orgasm - kidney and heart deficiency or kidney yang deficiency and minister fire
excessive sexual desire - liver or heart fire or kidney yin deficiency
headache soon after orgasm - rebellious qi of the penetrating vessel or heart fire
menses
(this is not significant for women who take contraceptive pills, have an IUD, or are multiparous)
cycle: always early - heat in the blood or qi deficiency
cycle: always late - blood deficiency, stagnation of blood or cold
cycle: irregular sometimes early and sometimes late - stagnation of liver qi, liver blood stasis, spleen qi deficiency, kidney qi deficiency
amount: heavy loss of blood
amount: scanty periods - blood deficiency, stagnation of blood or cold
color: dark-red or bright-red color - heat in blood
color: pale blood - blood deficiency
color: purple or blackish blood - stasis of blood or cold
fresh-red blood - empty-heat from yin deficiency
quality: congealed blood with clots - stasis of blood or cold
quality: watery blood - blood or yin deficiency
quality: turbid blood - blood heat or stagnation of cold
pain: before periods - stagnation of qi and blood
pain: during periods - blood heat or stagnation of cold
pain: after periods - blood deficiency
leukorrhea
color: white discharge - cold d/t spleen or kidney yang deficiency, external cold-damp, or sometimes liver qi stagnation
color: yellow discharge - heat pattern, usually d/t damp heat in the lower burner
color: greenish discharge - liver channel damp heat
color: red and white discharge - damp heat
color: yellow discharge with pus and blood in postmenopausal women - toxic damp heat in uterus
watery consistency: - cold-damp pattern
thick consistency:- damp heat pattern
fishy smell - cold damp pattern
leathery smell - damp heat pattern
pregnancy
infertility d/t empty conditions - blood or kidney essence deficiency
infertility d/t full conditions - damp heat in the lower burner or blood stasis in the uterus
vomiting during pregnancy - stomach and penetrating vessel deficiency
miscarriage before three months - blood or essence deficiency associated with kidney deficiency
miscarriage after three months - liver blood stasis or spleen qi sinking
childbirth
nausea and heavy bleeding post-delivery-exhaustion of penetrating vessel
sweating and fever post-delivery - exhaustion of qi and blood
postnatal depression - blood deficiency, leads to heart blood deficiency
the types of tongues
-
heart
deep branchy goes to the root of the tonguekidney
terminates at the root of the tonguespleen
transverses the root of the tongue and spreads over its lower surface -
conditions of the tongue proper may reflect deficiency or excess of zang-fu organs and relative strength of the essential qi
conditions of tongue coating reflect depth and nature of invading pathogenic factors
observe the tongue in natural light
food or drugs may color the tongue coating
eating or drinking changes the thickness or moisture
-
pale
deficiency of yang qi
deficiency of qi and blood
red
with coating: interior excess heat
no coating: yin deficiency
red tip: ht fire, ht yin deficiency
red sides: liver fire or gb heat
deep red
exogenous febrile disease: invasion of ying & xue systems by pathogenic heat.
endogenous: yin deficiency with fire
purple
blue purple: stasis of blood due to hot or cold.
deep-blue purplish, also dry and lusterless - heat.
pale purplish & moist: cold, stasis of blood
purplish spots: stasis of blood
reddish purple: heat & stasis of blood
-
thin
thin, pale: deficiency of qi & blood.
thin, dry & deep, red tongue: hyperactivity of fire due to yin deficiency (body fluids consumed).
cracked
may be present in a normal person
deep red: excessive heat consuming body fluids.
pale: deficiency of blood
short horizontal cracks: stomach yin deficiency
center crack reaching tip: heart pattern
short cracks on sides: chronic spleen qi deficiency
swollen
delicate & pale with toothprints: yang deficiency of spleen and kidney
deep red, taking up entire space of the mouth: excessive heat in heart & spleen.
bluish purplish, dark: toxicosis
red or normal colored: damp heat
pale & damp: yang deficiency
thorny
papillary buds swell up and look like thorns.
thorny & red: accumulation of pathogenic heat in interior.
deviated
wind stroke or early threatening signs of wind stroke
interior wind
rigid
lacks flexibility, difficult to protrude, retract or roll.
exogenous febrile diseases: invasion of pc.by heat,retention of turbid phlegm, or excessive pathogenic heat consuming body fluids.
endogenous diseases: wind stroke or early threatening signs of wind stroke
flaccid
weak in motion.
extreme deficiency of qi and blood, or consumption of yin fluids.
pale: deficiency of qi & blood.
flaccid & deep red: collapse of yin
length
long: tendency to heat (heart heat).
short: pale & wet = cold. red & peeled = yin deficiency
spleen qi deficiency
toothmarked
quiverin
-
moist: normal tongue coating is moist an lustrous (normal body fluids). slippery coating/excessive moisture with saliva dribbling when tongue stuck out (severe case) - upward flooding of harmful water & cold damp.
dry: coarse & feels lacking moisture. consumption of body fluid due to excessive heat or consumption of yin fluid not allowing it to nourish upwards.
sticky: covered by a turbid layer of fine greasy substance and hard to scrub - retention of turbid damp & phlegm or retention of food
granular: granules are coarse, loose and thick like a residue of making soy and easily scrubbed - excessive yang heat brings the turbid qi in the stomach upwards, retention of turbid phlegm or retention of food.
peeled: “geographic tongue:” some coating peeled off - consumption of qi and yin in the stomach. “glossy tongue:” entire coating peels off leaving surface mirror smooth - sign of exhaustion of stomach yin and severe damage of the stomach qi.
thin: tongue proper can be seen indistinctly. generally present if superficial portion of body affected, or deficiency of antipathogenic qi. (thinning coating points to gradual elimination of pathogenic factor.)
thick: tongue proper cannot be seen at all. retention of damp, phlegm, or food in the interior, or inward transmission of disease. (thickening coating points to inward transmission of pathogenic factor from exterior.)
-
white: exterior cold syndromes. thin & white - normal or exterior cold syndromes. thick & white - interior cold syndromes.
yellow: interior syndromes & heat syndromes. deeper yellow - more severe pathogenic heat. light yellow - mild heat. deep yellow - more severe heat. burnt yellow - accumulation of heat
grey: interior heat or cold & damp syndromes. grey, yellowish & dry - consumption of body fluid due to excessive heat. grey, whitish & moist - retention of cold damp, or phlegm & fluid.
black: interior syndromes with extreme heat or excessive cold. severe stage of illness. black, yellowish & dry, with thorns - consumption of body fluids due to extreme heat. pale black & slippery - excessive cold due to yang deficiency
-
too wet: yang qi not transporting or transforming fluids
dry: full heat or empty heat
sticky or slippery: damp or phlegm
the types of pulses
-
easily felt with gentle touch
exterior conditions
superficial, large & weak
prolonged endogenous diseases, indicating outward floating of yang qi
floating at superficial level but empty at deep level, deficiency of yin
rare cases floating in interior conditions (anemia, cancer) due to deficiency of qi “floats to surface.”
-
felt only on heavy pressure
interior conditions
deep & forceful
interior excess conditions
deep & weak
interior deficiency type, deficiency of qi and yang
deep & full
stasis of qi and blood in the interior, or interior cold or heat
-
less than 4 beats per breath (60bpm)
cold
slow & forceful
interior syndrome of excess type, retention of yin cold
slow & weak
interior syndrome of deficiency due to deficiency of yang qi
-
more than 5 beats per breath (90 bpm)
heat
rapid & forceful
excess heat retained in the interior/antipathogenic qi is strong
rapid & weak
deficiency yin in prolonged illness, produces deficiency heat in interior
rapid, weak, & large (full)
outward floating of deficiency yang
-
forceless pulse felt on 3 regions at 3 levels
deficiency of qi & blood
-
forceful pulse felt on 3 regions at 3 levels
excess qi & blood
struggle with antipathogenic qi against hyperactive pathogenic factor
excess & rapid, full, hard, long
full heat
excess & slow
full cold
-
broad, large & forceful like roaring wave, which comes on powerfully and fades away.
excessive heat
-
fine thready, distinct & clear
deficiency due to overstrain & stress
deficiency of qi & blood & yin
internal dampness with severe deficiency of qi
-
superficial & thready, hits fingers without strength.
damp
-
deep & thready, hits fingers without strength.
deficiency of qi & blood & yang
-
smooth and flowing like pearls rolling on a dish.
smooth rounded, slippery to touch, oily.
phlegm, damp, or pregnancy
retained fluid
retention of food
excess heat
-
feels rough and uneven or jagged.
stagnation of qi & blood
impairment of essence
deficiency of blood
after profuse & prolonged sweating
-
taut, straight, and long like violin or guitar string
disorders of liver & gb
pain
retention of fluids
phlegm
-
feels tight and forceful like a stretched rope
cold interior or exterior
pain
retention of food
asthma from cold in lungs
stomach cold
-
hurried & rapid
irregular missed beats
excessive yang heat =
heart fire deficiency of heart qi
-
swelling & pain, stagnation of qi & blood
retention of phlegm or food
-
prostration
-
slow
irregular missed beats
excessive yin
accumulation of qi
retention of cold phlegm
stagnant blood
cold & deficiency of heart qi or heart yang
-
slow & weak
could be serious heart condition
serious internal problems of one or more yin organs
regular missed beats
declining zang qi
wind syndromes
pain
emotional fear & fright
traumatic confusions & sprains
-
heat pattern, extends slightly beyond normal pulse position
-
severe deficiency of qi, or deficiency of stomach qi
-
generally a healthy pulse
-
after hemorrhage. rapid and slightly hollow - forthcoming loss of blood
-
stretched like a drum. hard and tight on the superficial level, but empty at deep level. severe deficiency of kidney essence or yin
-
felth on the deep level, hard and wiry (string-taut). interior stagnation and pain. firm and slow - interior cold
-
only on superficial level. could be damp if in combination with a very empty (deficiency) condition.
-
deficiency of yang
-
severe deficiency of qi and blood, & kidney qi.
-
extreme deficiency of yang
-
trembles under the finger, round like a bean. shock, anxiety, fright or extreme pain. people with deep emotional shock.
-
excess of yang, with fire in the body exhausting the yin.
